
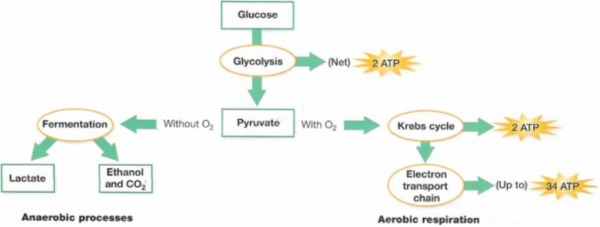
In total, the resulting product of aerobic cellular respiration from a single glucose molecule can be up to 38 ATP. Overall ETC produces water, NAD and FAD (which are both recycled back to glycolysis and Krebs cycle), and up to 34 ATP per one molecule of glucose!.Such reactions produce the majority of ATP during cellular respiration. In ETC, electrons are transferred from one complex to next where the electrons reduce oxygen to produce water.

CELLULAR RESPIRATION AN OVERVIEW SERIES
The Krebs cycle, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion, includes a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that result in the oxidation of the acetyl group to two carbon dioxide molecules.Krebs Cycle The Krebs Cycle (Source: Wikimedia) Also called as the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle, or simply the Citric Acid cycle, the Krebs cycle (identified by Hans Adolf Krebs) is an 8-step process that involves 18 different enzymes. In simpler terms, the pyruvate from glycolysis is oxidized (converted) to acetyl coA, one molecule of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and one molecule of carbon dioxide.Ģ.Such reaction is the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate by the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC).

After glycolysis, there is a so-called “link reaction” that occurs.However, two molecules are consumed during the preparatory phase, hence, resulting to a net of just two ATP molecules. While the above equation shows that glycolysis produce two ATP molecules, four molecules are actually produced during the entire process.Lactate production in humans when anaerobic respiration is used to maximize the power of muscle contractions.Īnalysis of results from experiments involving measurement of respiration rates in germinating seeds or invertebrates using a respirometer.C 6H 12O 6 + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 pyruvic acid, (CH 3(C=O)COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ Depending upon the oxygen demand, cellular respiration is of two types- aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells undergo cellular respiration. Use of anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking. In cells, cellular respiration is the pathway of yielding energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ĪTP from cell respiration is immediately available as a source of energy in the cell.Īnaerobic cell respiration gives a small yield of ATP from glucose.Īerobic cell respiration requires oxygen and gives a large yield of ATP from glucose. Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
